All The Things You Will Need To Know About
Overview

Heel pain is usually felt either under the heel or just behind it. Heel pain has a prevalence of 3.6%. US studies estimate that 7% of older adults report tenderness under the heel. Plantar fasciitis is estimated to account for 8% of all running-related injuries. There are 26 bones in the human foot, of which the heel is the largest. Pain typically comes on gradually, with no injury to the affected area. It is often triggered by wearing a flat shoe. In most cases the pain is under the foot, towards the front of the heel. The majority of patients recover with conservative treatments within months. Home care such as rest, ice, proper-fitting footwear and foot supports are often enough to ease heel pain. To prevent heel pain, it's recommended to reduce the stress on that part of the body.
Causes
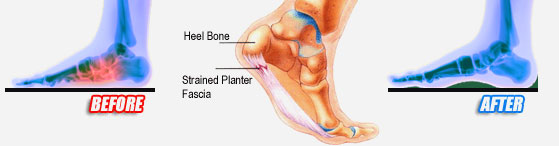
There are many causes of heel pain. However, plantar fasciitis, also known as heel spur syndrome, is the most common, by far. The pain is usually localized to the bottom of the heel towards the inside of the foot. The arch may also be painful. With this condition, pain is typically most severe with the first few steps after a period of rest. The pain my then subside and then return after extended periods of standing. There is usually no specific traumatic event that is responsible for the condition. It is usually the result of overuse, e.g. too much standing, walking or running. There are several common contributory factors such as weight gain, foot type, shoes. Flat shoes or going barefoot are the worst. Athletic shoes are usually the best. The plantar fascia is a fibrous band or ligament that connects the ball of the foot with the heel and helps to support the arch. When this band gets stretched too much or overused, inflammation results, often at the location where it attaches to the heel bone. A heel spur may develop as a result of chronic pulling by the plantar fascia. However, it should be noted that the pain is not caused by the spur. In fact, in some of the most severe cases, there is no spur at all. In other instances, an X-ray may be taken for an unrelated condition and an extremely large but non-painful spur may be seen. Other causes of heel pain include gout, stress fracture, bone tumors, nerve entrapment and thinning of the fat pad beneath the heel. Pain at the back of the heel is usually not plantar fasciitis. (Pain at the back of the heel is often due to an inflammation of the Achilles tendon, enlargement of the heel bone or bursitis.)
Symptoms
Depending on the specific form of heel pain, symptoms may vary. Pain stemming from plantar fasciitis or heel spurs is particularly acute following periods of rest, whether it is after getting out of bed in the morning, or getting up after a long period of sitting. In many cases, pain subsides during activity as injured tissue adjusts to damage, but can return again with prolonged activity or when excessive pressure is applied to the affected area. Extended periods of activity and/or strain of the foot can increase pain and inflammation in the foot. In addition to pain, heel conditions can also generate swelling, bruising, and redness. The foot may also be hot to the touch, experience tingling, or numbness depending on the condition.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of heel pain and heel spurs is made by a through history of the course of the condition and by physical exam. Weight bearing x-rays are useful in determining if a heel spur is present and to rule out rare causes of heel pain such as a stress fracture of the heel bone, the presence of bone tumors or evidence of soft tissue damage caused by certain connective tissue disorders.
Non Surgical Treatment
Once diagnosed, treatment for plantar fasciitis may include one or more of the following: advice on footwear, in particular use of arch-supportive footwear; avoid walking barefoot; stretching exercises, shoe modifications such as heel pads, taping and strapping, anti-inflammatories and orthotic devices to correct abnormal foot mechanics. Injection therapy with corticosteroids is only advisable if all the conservative treatment methods mentioned above have been exhausted due to undesired effects implicated with steroid infusion in the heels.
Surgical Treatment
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (EST) is a fairly new type of non-invasive treatment. Non-invasive means it does not involve making cuts into your body. EST involves using a device to deliver high-energy soundwaves into your heel. The soundwaves can sometimes cause pain, so a local anaesthetic may be used to numb your heel. It is claimed that EST works in two ways. It is thought to have a "numbing" effect on the nerves that transmit pain signals to your brain, help stimulate and speed up the healing process. However, these claims have not yet been definitively proven. The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) has issued guidance about the use of EST for treating plantar fasciitis. NICE states there are no concerns over the safety of EST, but there are uncertainties about how effective the procedure is for treating heel pain. Some studies have reported that EST is more effective than surgery and other non-surgical treatments, while other studies found the procedure to be no better than a placebo (sham treatment).
deelsonheels
Prevention
It is not always possible to prevent heel pain, but there are measures you can take to help avoid further episodes. Being overweight can place excess pressure and strain on your feet, particularly on your heels. This increases the risk of damaging your feet and heels. If you are overweight, losing weight and maintaining a healthy weight by combining regular exercise with a healthy, balanced diet can be beneficial for your feet. You can calculate your body mass index (BMI) to find out whether you are a healthy weight for your height and build. To work out your BMI, divide your weight in kilograms by your height in metres squared. A BMI of less than 18.5 means that you are underweight, 18.5-24.9 means that your weight is healthy, 25-29 means that you are overweight, 30-40 means that you are obese, over 40 means that you are morbidly obese. You can also use the BMI healthy weight calculator to work out your BMI.

Heel pain is usually felt either under the heel or just behind it. Heel pain has a prevalence of 3.6%. US studies estimate that 7% of older adults report tenderness under the heel. Plantar fasciitis is estimated to account for 8% of all running-related injuries. There are 26 bones in the human foot, of which the heel is the largest. Pain typically comes on gradually, with no injury to the affected area. It is often triggered by wearing a flat shoe. In most cases the pain is under the foot, towards the front of the heel. The majority of patients recover with conservative treatments within months. Home care such as rest, ice, proper-fitting footwear and foot supports are often enough to ease heel pain. To prevent heel pain, it's recommended to reduce the stress on that part of the body.
Causes
There are many causes of heel pain. However, plantar fasciitis, also known as heel spur syndrome, is the most common, by far. The pain is usually localized to the bottom of the heel towards the inside of the foot. The arch may also be painful. With this condition, pain is typically most severe with the first few steps after a period of rest. The pain my then subside and then return after extended periods of standing. There is usually no specific traumatic event that is responsible for the condition. It is usually the result of overuse, e.g. too much standing, walking or running. There are several common contributory factors such as weight gain, foot type, shoes. Flat shoes or going barefoot are the worst. Athletic shoes are usually the best. The plantar fascia is a fibrous band or ligament that connects the ball of the foot with the heel and helps to support the arch. When this band gets stretched too much or overused, inflammation results, often at the location where it attaches to the heel bone. A heel spur may develop as a result of chronic pulling by the plantar fascia. However, it should be noted that the pain is not caused by the spur. In fact, in some of the most severe cases, there is no spur at all. In other instances, an X-ray may be taken for an unrelated condition and an extremely large but non-painful spur may be seen. Other causes of heel pain include gout, stress fracture, bone tumors, nerve entrapment and thinning of the fat pad beneath the heel. Pain at the back of the heel is usually not plantar fasciitis. (Pain at the back of the heel is often due to an inflammation of the Achilles tendon, enlargement of the heel bone or bursitis.)
Symptoms
Depending on the specific form of heel pain, symptoms may vary. Pain stemming from plantar fasciitis or heel spurs is particularly acute following periods of rest, whether it is after getting out of bed in the morning, or getting up after a long period of sitting. In many cases, pain subsides during activity as injured tissue adjusts to damage, but can return again with prolonged activity or when excessive pressure is applied to the affected area. Extended periods of activity and/or strain of the foot can increase pain and inflammation in the foot. In addition to pain, heel conditions can also generate swelling, bruising, and redness. The foot may also be hot to the touch, experience tingling, or numbness depending on the condition.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of heel pain and heel spurs is made by a through history of the course of the condition and by physical exam. Weight bearing x-rays are useful in determining if a heel spur is present and to rule out rare causes of heel pain such as a stress fracture of the heel bone, the presence of bone tumors or evidence of soft tissue damage caused by certain connective tissue disorders.
Non Surgical Treatment
Once diagnosed, treatment for plantar fasciitis may include one or more of the following: advice on footwear, in particular use of arch-supportive footwear; avoid walking barefoot; stretching exercises, shoe modifications such as heel pads, taping and strapping, anti-inflammatories and orthotic devices to correct abnormal foot mechanics. Injection therapy with corticosteroids is only advisable if all the conservative treatment methods mentioned above have been exhausted due to undesired effects implicated with steroid infusion in the heels.
Surgical Treatment
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (EST) is a fairly new type of non-invasive treatment. Non-invasive means it does not involve making cuts into your body. EST involves using a device to deliver high-energy soundwaves into your heel. The soundwaves can sometimes cause pain, so a local anaesthetic may be used to numb your heel. It is claimed that EST works in two ways. It is thought to have a "numbing" effect on the nerves that transmit pain signals to your brain, help stimulate and speed up the healing process. However, these claims have not yet been definitively proven. The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) has issued guidance about the use of EST for treating plantar fasciitis. NICE states there are no concerns over the safety of EST, but there are uncertainties about how effective the procedure is for treating heel pain. Some studies have reported that EST is more effective than surgery and other non-surgical treatments, while other studies found the procedure to be no better than a placebo (sham treatment).
deelsonheels
Prevention

It is not always possible to prevent heel pain, but there are measures you can take to help avoid further episodes. Being overweight can place excess pressure and strain on your feet, particularly on your heels. This increases the risk of damaging your feet and heels. If you are overweight, losing weight and maintaining a healthy weight by combining regular exercise with a healthy, balanced diet can be beneficial for your feet. You can calculate your body mass index (BMI) to find out whether you are a healthy weight for your height and build. To work out your BMI, divide your weight in kilograms by your height in metres squared. A BMI of less than 18.5 means that you are underweight, 18.5-24.9 means that your weight is healthy, 25-29 means that you are overweight, 30-40 means that you are obese, over 40 means that you are morbidly obese. You can also use the BMI healthy weight calculator to work out your BMI.